The world of audio mixing is a broad and exciting subject. There are several types of audio mixers, and each type has its advantages and disadvantages.
The best artists in the world are always looking for the most advanced audio mixers in the market to create the best possible mixes. From concerts and live gigs to TV sets and recording studios, a sound mixer should provide top-notch audio quality for music, TV, podcasts, and film.
Charged with the responsibility of picking up sound signals from microphones, musical instruments, and other sources, a mixing console blends and tweaks two or more sound signals. Then it sends the polished audio to the loudspeakers, amplifiers, or recording systems.
There are different types of audio mixers available in the market today. But the three main ones are analog, digital, and powered audio mixers. In this article, we’ll walk you through the differences between the three types of mixing consoles, the advantages and disadvantages of each class, and everything in between.
Analog Mixers
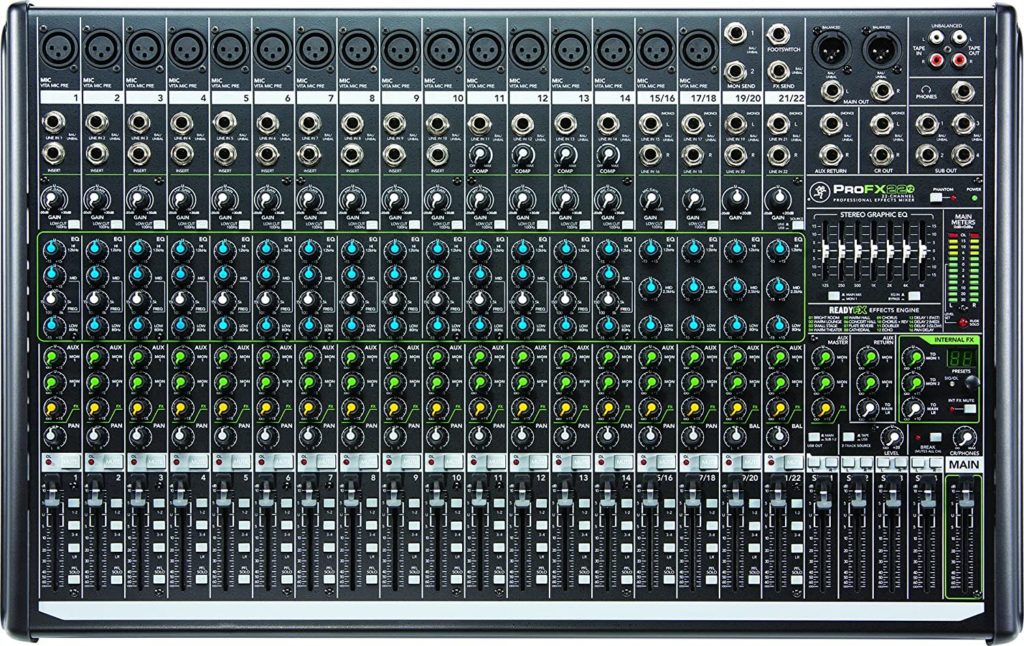

An analog mixer is what generally comes to mind when most people think of a mixing desk. It has a standard appearance, and a pretty unified layout such that any person with some knowledge operating a mixing desk can get hold of one and get going immediately.
Analog mixers use analog electronic devices to operate. They have one control per function, all of which are visible and accessible on the control panel.
You can quickly see what’s happening in the mixer and make adjustments where necessary. These mixers are perfect for live sound and for recording too.
Concerning cost, analog mixers generally cost less than their digital counterparts. Still, they lack the kind of automation you may need for complicated setups. Plus, they do not have wireless connectivity for remote control, which means you have to be at the board all the time.
Aside from that, analog mixers have less onboard sound effects than digital models. If you want to get advanced audio effects and sound processing systems, you have to buy external hardware for that.
Advantages of Analog Mixers
With that said, analog mixers have numerous advantages. Some of these include:
- They are cheap and inexpensive to buy
- They are user-friendly. Once you get the hang of an analog mixer, you can efficiently operate any other analog mixer. First-time audio mixer users usually find it easier to learn and operate.
- It is also straightforward to correct any problems with the flow of the sound. This is because all controls are visible and easily accessible on the control panel
- Another perk worth mentioning is the fact that you can quickly and easily set up a live mix.
Disadvantages of Analog Mixers
Analog mixers also have some disadvantages, which include:
- Depending on the number of channels, they could be bulky, which means carrying them from one place to another is a daunting task
- The effects and audio processing features in analog mixers are very limited.
- Due to their lack of wireless connectivity, most of the time, they require long cable runs, because it might not be practical to install them on stage
- Unlike digital mixers, there’s no feature to allow you to recall or reprogram any of the previous gigs. This makes using an analog mixer tiring because you have to create new mixes each time you set up.
READ: How to Connect an Analog Mixer to an Audio Interface
Digital Mixers
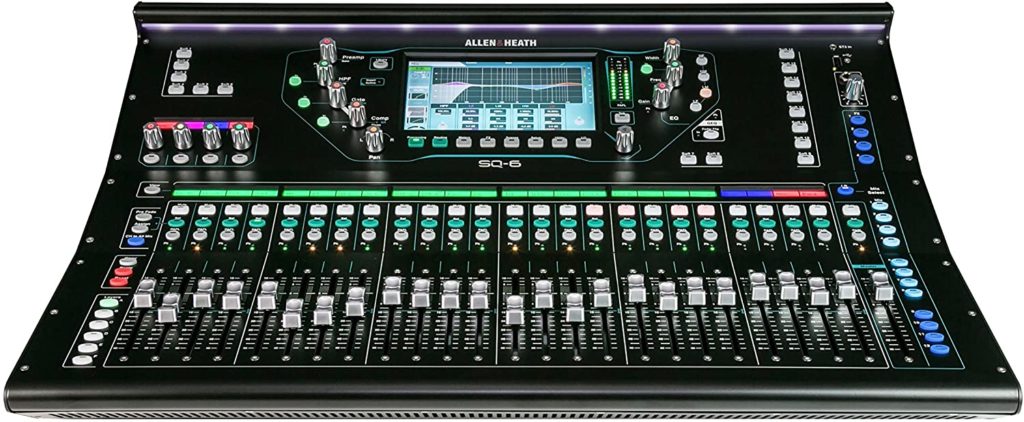

Digital mixers have a wider variety of control functions. You can pre-program, save, and recall setups, which is convenient if you play with the same band regularly. This is also a plus for when you need to make a quick set up change in the middle of the event.
Most digital mixers also come with wireless connectivity to connect it to an iPad or smartphone for remote control. This means that you don’t have to be positioned in one place the entire time. You are free to walk all over the room while mixing on your phone or tablet, ensuring the music is heard everywhere.
It’s almost impossible to walk around when mixing from an analog device because you’ll need a bulky extension cable, commonly called a “snake,” which is also expensive to buy. But even with it, you’ll still have to stay in one spot.
With digital mixers, you have more onboard sound effects on every channel. You don’t have to buy separate audio equipment to get better sound effects and advanced signal processing features.
Most of the time, you can get upgraded effects and signal processing features by downloading updates from the manufacturer.
However, making any adjustments in a digital mixer may pose a significant challenge if you are not experienced with it. That’s because you’ll have to first browse through several menu options on the touchscreen before you can make any changes in a specific channel. And if you want to make more than one change at a go, you’ll have to pre-program the changes for faster access.
Advantages of a Digital Mixer
- It’s easy to pre-program and recall settings whenever you want to use them. This is very convenient in large live setups when you need to change the atmosphere of an event quickly.
- Digital mixers can accommodate more external sound sources even though they are smaller than their analog counterpart.
- Furthermore, signals processed by digital mixers are more resistant to picking line noise.
- Unlike analog mixers that have one control per function, digital mixers can perform a variety of tasks because each control offers several features for different purposes.
- They can be used to perform multi-track recordings.
- Finally, digital mixers are compact and portable, which makes carrying them from one point to another relatively easy.
Disadvantages of Digital Mixers
- One of the most significant disadvantages of digital mixers is their cost. They are very expensive to acquire thanks to their sophistication and the fact that they can perform a variety of functions with just one device
- Digital mixers are also difficult to operate. Even a veteran can be thrown off by the sheer amount of sophistication they have. Learning how to use and operate one digital mixer doesn’t mean you can automatically operate another digital mixer.
READ: Mixing Console Basics
Digital Mixer vs. Analog Mixer – What’s the Difference?
1. Pricing
Perhaps, the biggest difference between analog and digital mixers is their cost. While analog mixers are generally cheap, their digital brethren are expensive.
But digital mixers often come with many extras such as gates, effects, compressors, and many more signal processing features that justify the price difference.
2. Ease of Use
Analog mixers are usually easier to learn and operate even for beginners. Signal processing is straightforward because every input directly relates to the control it is fed into.
For instance, if you connected a guitar into input 1, then the entire control panel in channel 1 will affect the guitar and only that guitar.
Digital mixers, on the other hand, can be confusing. Even experienced people can get mixed up with all the customization going on; because you can route any input to any control.
For instance, if you connect a guitar to the first input, that input can be routed to any available output without physically connecting any cable to route the signal.
You can even assign or route a specific channel to any other channel using the touchscreen to send the commands.
Conversely, most digital mixers allow you to pre-program, save, and recall settings. This is hands down the most beautiful thing about digital models as it helps you save time in large event setups.
Take, for instance, bands that use the same music configuration for all their gigs, all they have to do is set up, plug in mics and instruments and recall their past settings, including their favorite sound effects. How cool, huh!
Likewise, venues that have several bands performing can also benefit from this cool feature. Because you can quickly save the settings of each band and recall them every time they come on stage.
3. Sound Quality
Quality of sound is another big consideration when it comes to the analog vs. digital debate. At the high end of the pricing spectrum, digital mixers have just about matched the quality of sound produced by superior analog models.
However, at the bottom of the pricing spectrum, you’ll realize analog models are better in all aspects, especially sound-wise.
4. Availability of Spare Parts
Another thorny factor that most people overlook is the issue of repairs. Taking all things to consideration, an analog mixer that is about 30 years old will likely be repaired more easily than a digital one, as the parts used to manufacture are likely to still be available in the market today.
However, we’ve often heard of digital mixers that are only 5 years old that have needed repairs only to realize that the parts are not being produced anymore or there are no spares available to do the necessary repairs. That means that you would have to buy a new mixer.
Which one is Better? – Which One Should You Pick?
If you’re ever faced with the decision of whether to go digital or stick with analog, just know that one is not necessarily superior to the other. What works for a solo artist may not necessarily work for a bigger setup.
That being said, both analog and digital mixers are very popular. And all types of audio mixers have their unique advantages and disadvantages. It all comes down to your personal preference and for what you’ll be using the mixing console.
Powered Mixers
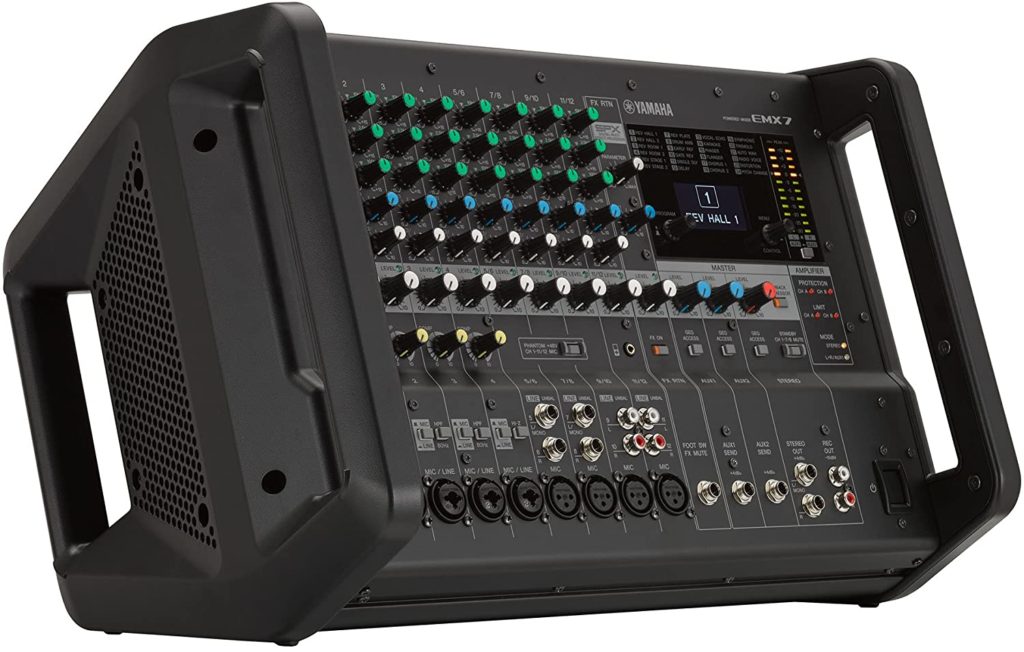

Another type of audio mixers are powered mixers. A powered mixer is basically an analog mixer but with the added advantage of built-in power amplifiers. Most powered mixers come with two amp channels and can be plugged in with two speakers or one speaker and one monitor.
They are usually easy to set up and use. They are also pretty compact, which means they are easy to transport.
Powered mixers also feature line-level outputs allowing you to add more powered speakers and monitors easily.
Advantages of Powered Mixers
- Simple to set up and operation
- Portability
- All-in-one integration
Disadvantages of Powered Mixers
- If one part of it fails, you’ll need to replace the whole unit
- Unlike analog and digital mixers, you don’t get a variety of features
READ: How to Set Up a Stage Sound System
How to Choose the Right Audio Mixer Depending on Your Needs
Besides price, there are many other things to consider when choosing an audio mixer. And given the different types of audio mixers in the market today, we compiled some of the first and most important things to look for when shopping for one:
1. Purpose
What will you be using your mixer for? Recording, live plays, or both? If you’ll be using your mixer for recording, you should take into consideration the quality of mic preamp as well as the ability to pair up with a variety of external hardware.
If you’ll be using it for live play, you’ll want to make sure it’s compatible with your sound systems and can accommodate the needs of your band. Another critical consideration is ruggedness – weak and fragile equipment won’t last long, especially if you go from gig to gig.
2. I/O and Channels
How many mics will you connect to the mixer? For instance, if you’re using condenser mics, you’ll need to have mic inputs with phantom power.
If you’re using stereo instruments such as keyboards, you’ll need enough stereo inputs to connect them.
If you plan to connect guitars directly, you’ll need enough inputs to house them too. It’s always advisable to get enough I/O and channels to accommodate your current and future needs because bands tend to add gear and players over time.
3. EQ Needs
When recording in a studio, you’ll need to fine-tune the sound to enhance audio quality. Multiband equalizers and filters are required to create an excellent recording, and a digital mixer is the best choice in this case.
On the other hand, if all you’re doing is some simple sound mixing, basic control over high, mid and bass frequencies is all you need, then an analog mixer would be the best choice
4. Sound Processors and Effects
Do you heavily rely on external effects pedals, mic preamps, and other sound processing equipment to get better audio quality? If this is the case, you don’t need a unit with internal sound effects and processors.
That said, a mixer with internal sound effects and audio processing is a handy companion and makes for a compact and portable unit when performing live.
5. Buses and Signal Routing:
You’ll need more buses and signal paths if you’ll be using your mixer for large live events or multiple channel recordings. So consider that when buying your next audio mixer.
Takeaway
It all comes down to personal preference and what you intend to use an audio mixer for. We hope that this article on the different types of audio mixers will help you weigh the advantages and disadvantages of analog, digital and powered mixers and choose the right option for your needs.
