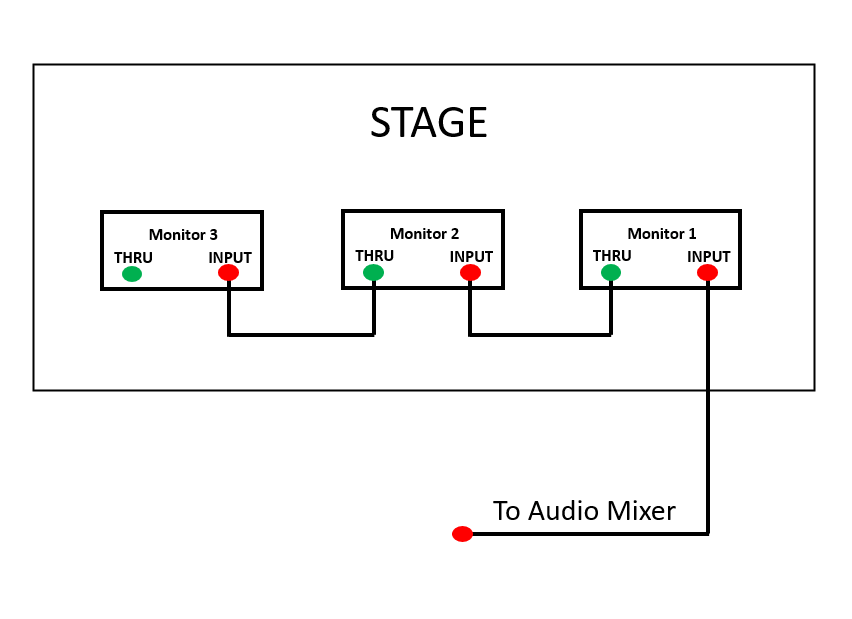
When setting up a PA system for a party or live event, you’ll see lots of wires going everywhere. Thanks to wireless microphones, fewer cables are used nowadays in setups. Still, speakers always need a signal cable to run from the main audio mixer to them.
These cables are usually long, and they create a lot of inconveniences, including tripping hazards for the people walking around the venue. Wouldn’t it be awesome to have a wireless PA speaker system so that no cable runs are needed anymore?
In today’s post, I will present a couple of ways of how to make powered speakers wireless. I will also discuss if it’s possible to use a Bluetooth transmitter on a mixing console to send the signal wirelessly to Bluetooth-capable PA speakers.
Exploring What Options Are Available On the Market
The truth is that there aren’t many options for converting powered PA speakers into wireless. For some reason, manufacturers have lots of options for wireless microphones but none for speakers.
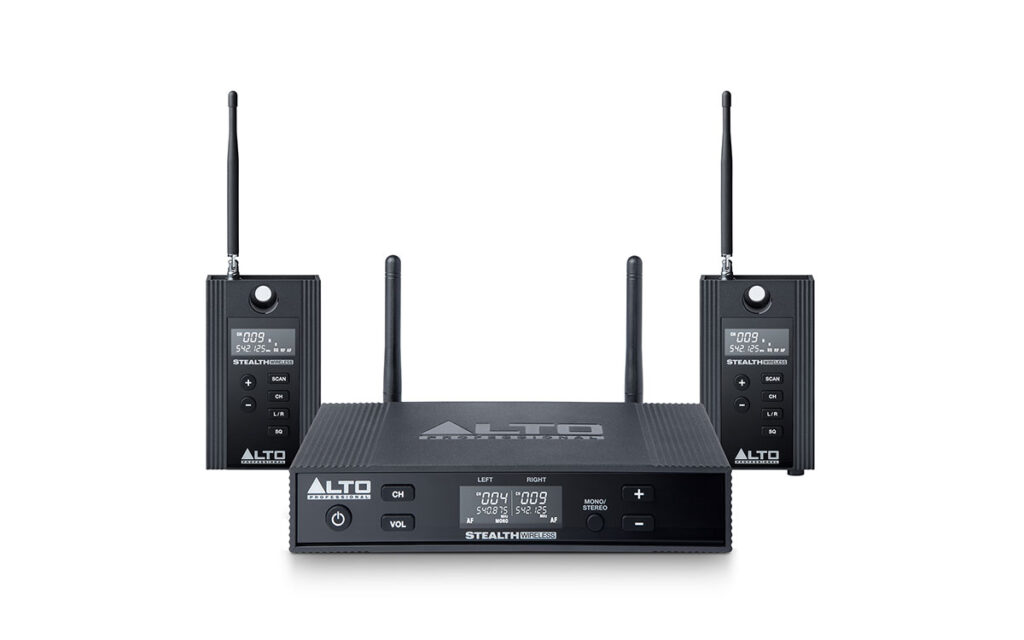
There is a company called Alto that makes a wireless stereo system for active speakers, the Alto Stealth Pro Wireless System for Loudspeakers. This system comes with one stereo RF transmitter and two receivers, one for each speaker.
They give you the option of buying extra receivers called Stealth Expanders to use them in bigger setups. If you were asking yourself how to make your pa speakers wireless, this is the best option.

Pro-Level Wireless Speaker System
The Alto Stealth Pro wireless system is excellent because it comes with everything you need to make any powered or passive speaker wireless, and once and for all, get rid of all those audio cables and step into the world of wireless sound. The only problem is that it is a bit pricey.
The Alto Stealth Pro is designed for active speakers. Still, it can accommodate passive speakers as well, depending on your setup. Plus, it is compatible with devices such as mixers, DJ controllers, karaoke devices, or any other audio source.
Features
The transmitter offers two combo XLR-1/4” inputs to accommodate different types of devices. With the available 16 UHF channels, you can be assured that interference will be at a minimum, plus it comes with three controlled squelch settings.
The system’s frequency range is between 540-570 MHz, which falls within the legal wireless frequency range. The operating range is 330 ft (100 m) line of sight, and its frequency response goes between 50Hz-17kHz.
With the dual-channel UHF transmission and True Diversity reception, you can be sure that you will get the best coverage within its operating range for all of your events.
Both the transmitter and receiver units have an intuitive front-panel LCD screen that provides instant confirmation of the configuration. It displays the RF frequency and channel as well as the AF signal level for each channel.
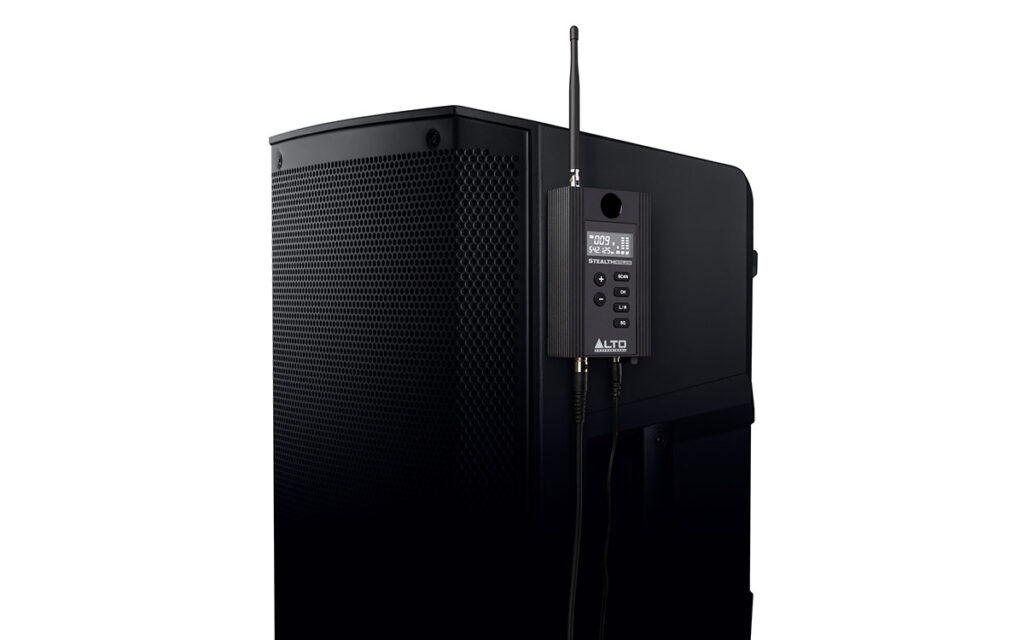

Content of the Box
The Alto Stealth Pro wireless speaker system comes with everything you need to setup right away. In the box you will get:
- Stealth Pro Transmitter (x1)
- Stealth Pro Receiver (x2)
- Power Adapters (x3)
- Mini-XLR to XLR Cables (x2)
- Removable Antennas (x6)
- M10 Rigging Bolts (x2)
- Short Rack Ear (x2)
- Long Rack Ear (x1)
- M4 Rack Ear Coupling Bolts (x5)
- Center Coupling Bracket (x1)
- User Guide
- Safety & Warranty Manual
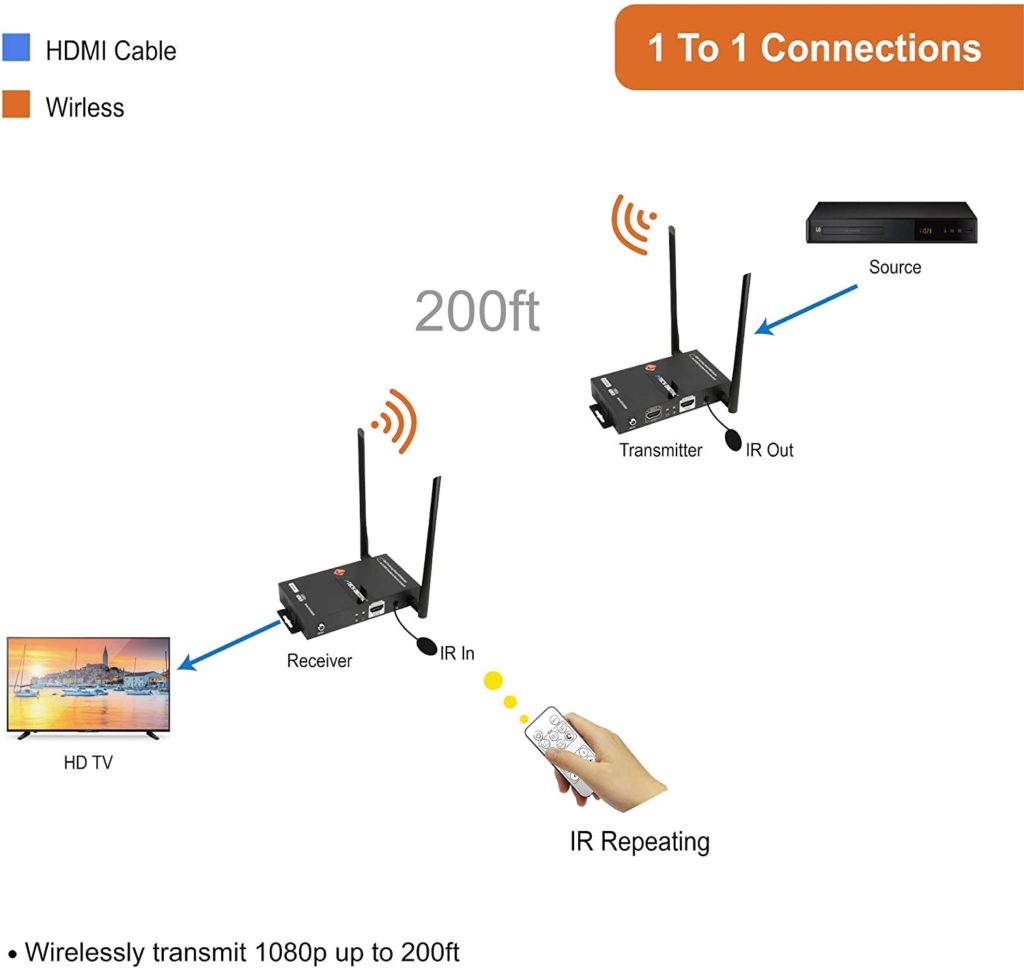
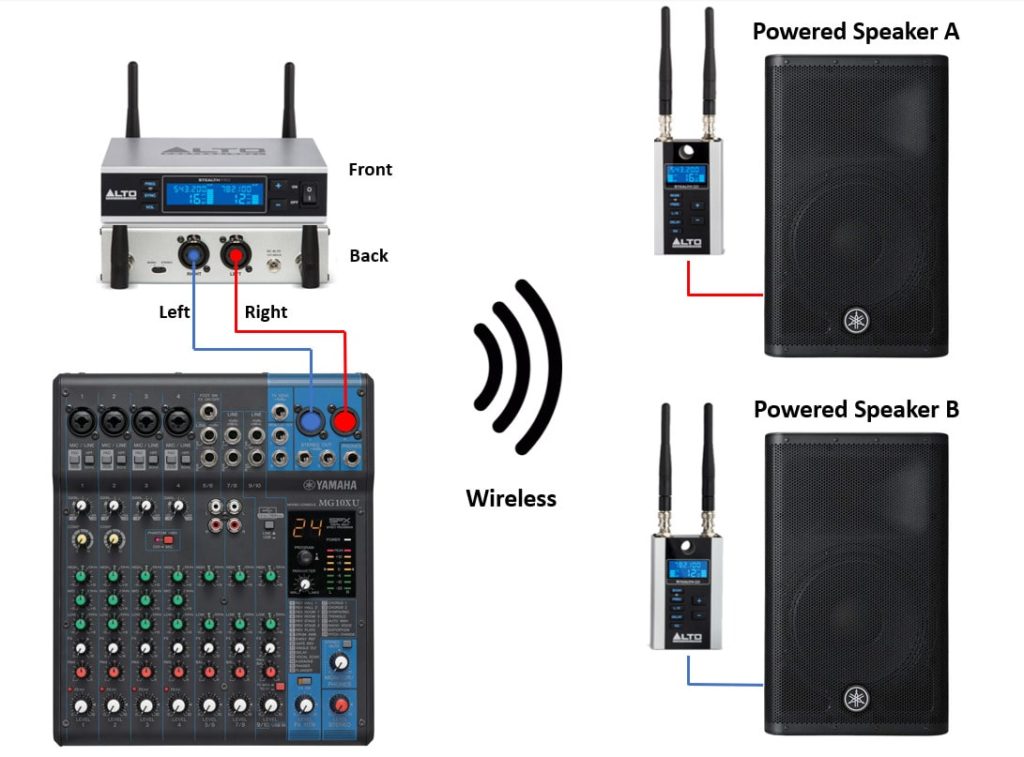
Steps for Making Active Speakers Wireless
To install and use the Alto Stealth Pro wireless system for powered speakers, follow these steps:
- With the mixer, transmitter, receivers, and speakers turned Off, locate the “Main Out” or “Stereo Out” connectors in the mixing console.
- Choose between XLR or 1/4” jack to connect between the output of the mixer and the input of the transmitter.
- Use the included mini-XLR cable to connect from the output of the receiver unit to the input of the powered speaker.
- After connecting the XLR cable to the speaker, turn the volume on the speaker halfway and turn it on. Also, turn on each receiver unit.
- Now you can turn on the transmitter unit and the mixer.
- On the transmitter, set the mode to Mono or Stereo. If your mixer is stereo, choose the stereo mode.
- Turn the volume of the left and right channels halfway on the transmitter unit using the buttons on the front panel.
- Select a broadcast channel on the transmitter and make sure to select the same channel number on the receiver units.
- Play some music on the mixer, and slowly increase the main volume until you hear a sound coming out of the speakers.
- Adjust the volume of the speakers or transmitter unit until you are satisfied with it and perform a soundcheck.
Here is a diagram for your reference on how to make active pa speakers wireless.
Steps for Making Passive Speakers Wireless
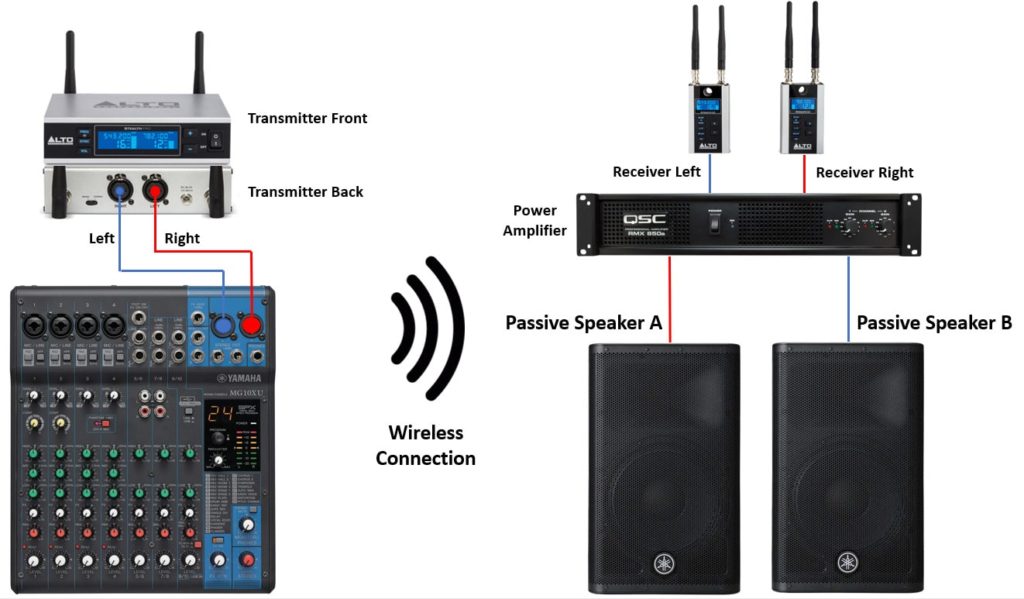
As mentioned previously, the Alto Stealth Pro wireless system can also be used for turning passive PA speakers wireless. To do that, follow these steps.
- Make sure all of the equipment are turned off before starting to connect things up.
- Locate the “Main Out” or “Stereo Out” in the mixing console.
- Use an XLR or 1/4” jack cable for connecting between the output of the mixer and the input of the transmitter.
- Use the included mini-XLR cables to connect the output from the receiver units to the input of the power amplifier.
- After connecting the XLR cable to the amplifier, turn the volume on the amp to halfway.
- Connect the passive speakers to the amp and turn it on. Don’t forget to also turn on the receiver units.
- Now you can turn on the transmitter unit and the mixer.
- On the transmitter, set the mode to Mono or Stereo, if your mixer is stereo, choose the stereo mode.
- Turn the volume for the left and right channels halfway on the transmitter unit using the buttons in the front panel.
- Select a channel on the transmitter and make sure to select the same channel number on the receiver units.
- Play some music on the mixer, and slowly increase the main volume until you hear a sound coming out of the speakers.
- Adjust the volume of the power amplifier or transmitter unit until you are satisfied with it and perform a soundcheck.
Here is a diagram for connecting passive speakers to a mixer wirelessly, use it for your reference.
Another Wireless Solution from Alto Professional
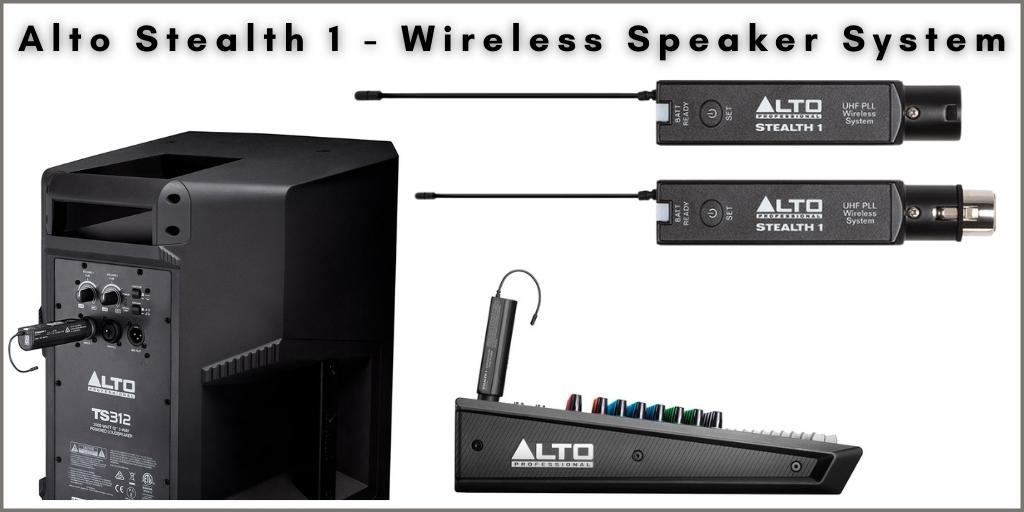

Alto Professional provides another wireless solution for converting any active speaker to wireless, the Alto Stealth 1 Wireless system. This is a more affordable option, but it also delivers excellent results.
Just like the Pro system, it’s easy to set up. The Stealth 1 is a mono UHF wireless system offering balanced XLR connectors for the transmitter an receiver.
Each set comes with one transmitter and one receiver, which means that if you have a stereo setup, you would need to buy two sets. Buying two set will cost you about half of what the Stealth Pro costs.
The audio quality is as good as if the system was connected using wires but without the hassle. This wireless system uses one AA battery for the the transmitter and another AA for the receiver which gives you 4+ hours of operation.
The system uses the reliable UHF band between 542-566 MHz, which falls within the legal wireless frequency range in the US and Canada. The operating range is 100ft (30 m) line of sight, and its audio frequency response is between 50Hz-17kHz.
If you decide to go with this unit, the setup would be very simple. Connect the transmitter on the “Main Outs” of the mixing console and the receiver on the input channel of the powered speaker. Set the same channel on the transmitter and receiver and you are done.
Another Option for Making Any Powered PA Speakers Wireless
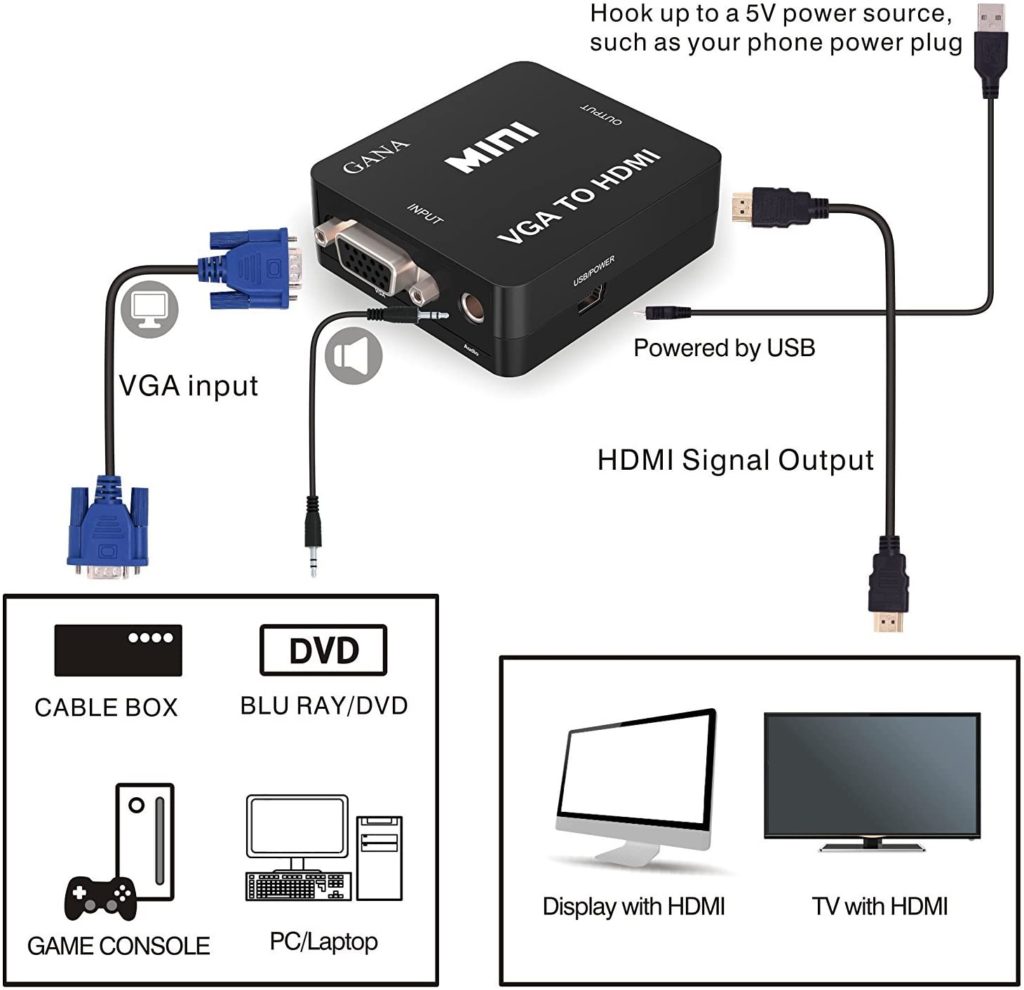
To make any powered speaker wireless, you need to transmit the signal from the mixer or DJ controller to the speaker wirelessly. To achieve this, you can use a wireless instrument set.
I have personally used this option as a more affordable way of making my powered speakers wireless. Although it is more affordable, it’s not going to be as good as the Alto Stealth Pro system.
Using a Wireless Instrument System for Making an Active Speaker Wireless
Wireless instrument systems are designed to make any pluggable instrument such as guitar, bass, or electric violin, etc. wireless. They have an input level control knob to adjust the audio level that comes in.
You can use any wireless instrument system from any brand to try this, but I am going to describe the process using the AKG Perception Wireless Instrument Set because I have used it in my setup and it delivers a good result.
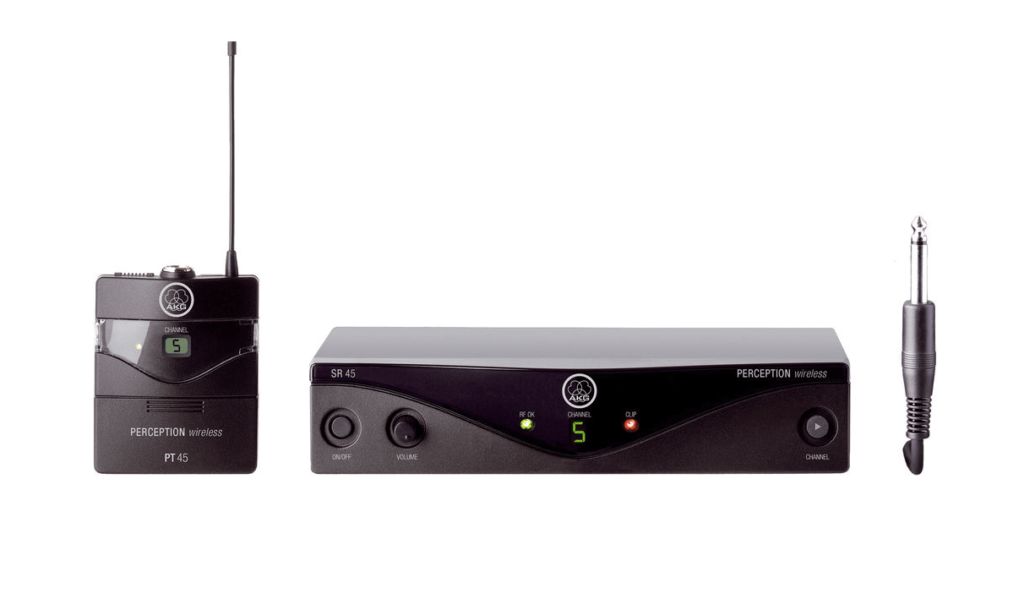

The AKG Perception is a wireless system designed to be used as a wireless instrument system. But thanks to its high-quality audio broadcast and wide frequency range, it can be used for our purpose.
For converting your PA speakers to wireless, you would need two units, one to send the signal to the left speaker and one for the right speaker.
This unit ships with one transmitter, one receiver, and a 1/4” jack to mini XLR cable.
It provides 8 Selectable Frequencies that range between 530 – 560 MHz and an audio bandwidth of 40 Hz to 20 kHz. This system also falls within the legal wireless frequency range and it offers an operating range of 100ft (30.5 m) line of sight.
The transmitter pack uses 1×1.5V AA Battery for up to 10 hours of operation, making it very efficient for any live setup.
By setting up the system correctly, you can use it to broadcast the mixing console’s audio signal to a speaker as long as it is within the system’s range.
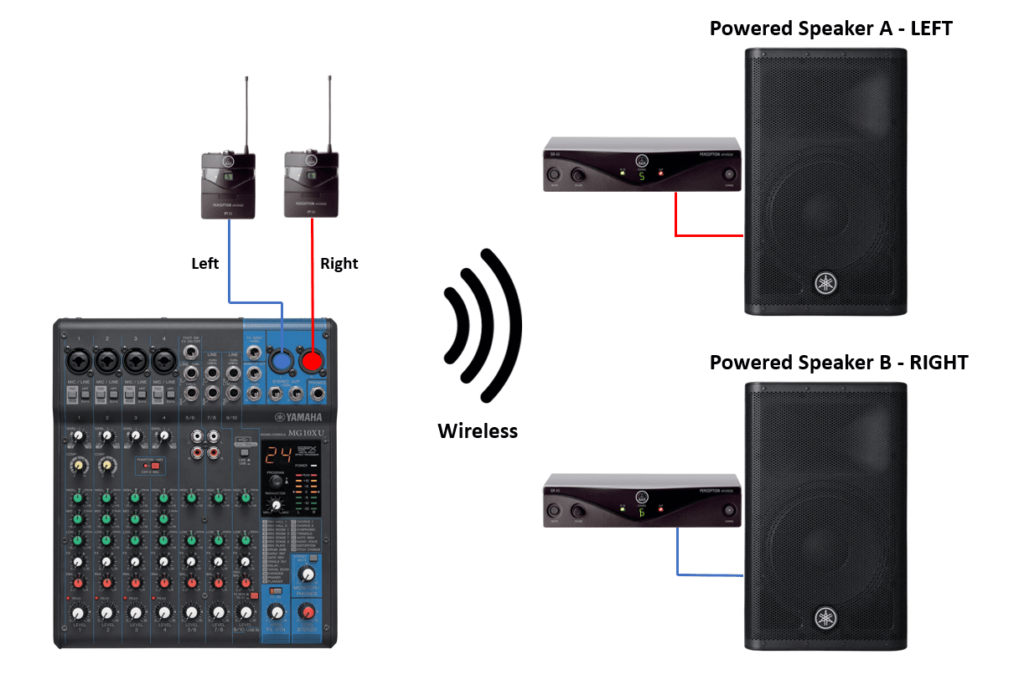
Steps for Making Active Speakers Wireless Using a Wireless Instrument Set
The following steps explain how to use the AKG Perception wireless instrument set to make PA speakers wireless:
- I always recommend having all the equipment turned off before starting any setup.
- Before connecting the transmitters’ bodypack to the mixer, make sure to adjust the input level. Turn the knob down to about 25% of the volume. Make sure that both transmitters are set to the exact same level. To do that, open the battery cover and look for a small gray knob that is located in the upper left corner above the battery. See the image below for your reference.
- Connect the transmitters’ bodypack to the mixer’s outputs using the provided 1/4” Jack cable that comes with the unit.
- Take the receiver and place it next to the active speaker. Use the corresponding cable to make the connection between the receiver and the speaker.
- Make sure to set one channel for the left and a different channel for the right speaker. For example, if you set channel 5 on the transmitter and receiver for the “Left” speaker, use channel 7 on the transmitter and receiver for the “Right” speaker. The good thing is that you get eight channels to choose from.
- Set the volume of the speaker to about halfway. If, after testing, you feel that the volume is too low, increase it to your likings.
- Turn on the mixer, transmitters, receivers, and speakers to do a soundcheck.
- Slowly increase the volume on the mixer. If you get to the point that the sound is too low, then try increasing the volume on both transmitters to see if it sounds better. Make sure not to saturate the input of the transmitters, because it will sound distorted. For better results, if you start hearing distortion, put the volume on the transmitters back to the way it was, and try increasing the volume of each speaker instead.
- Perform soundchecks using microphones and music to see how the system reacts, if you are not happy with it, try adjusting until you find the sweet spot. It might take a few sound tests before you get the ideal setting.
Adjusting the Input Audio Level on the AKG Perception Transmitter

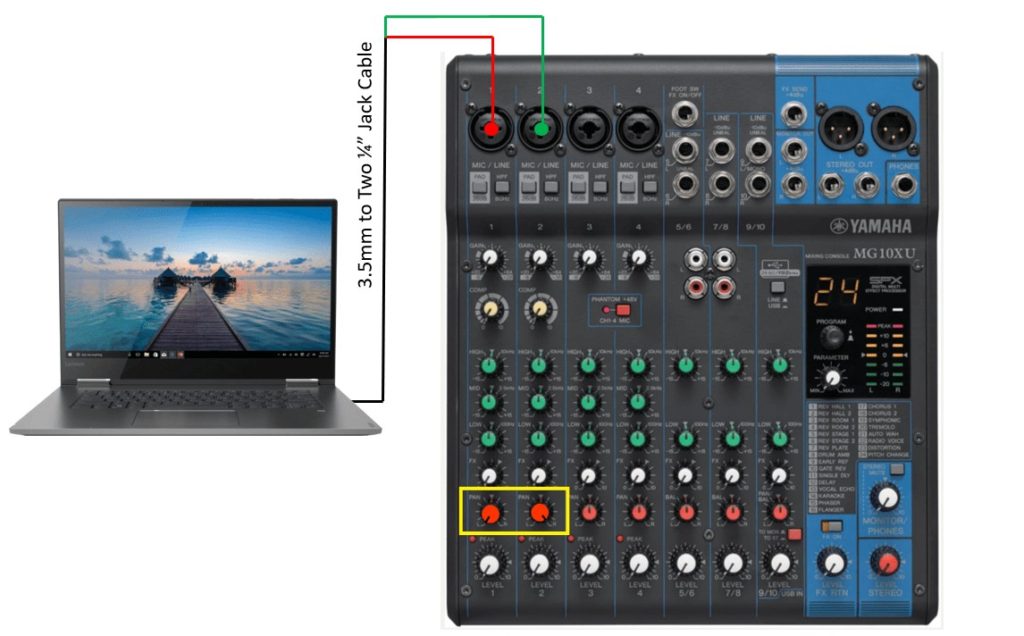
Connection Diagram Using the AKG Perception Instrument Set
Below is the diagram for making powered PA speakers wireless using the AKG Perception wireless instrument set.
Using a Bluetooth Transmitter and Bluetooth capable PA speakers
You might ask the question if it’s possible to use a Bluetooth transmitter on a mixing console to send the signal wirelessly to Bluetooth-capable PA speakers.
In theory, it’s possible to use a stereo Bluetooth transmitter to connect the output of your mixer to it, then pair the Bluetooth-capable PA speakers, but I don’t recommend it.
The problem is something called latency, which is a delay between the time the signal is generated in the mixer and how long it takes for it to sound on the speaker. Let me explain what goes behind the scenes.
Let’s say that a person is talking through a microphone, the signal goes from the mic to the mixer, then out to the Bluetooth transmitter. The signal is then digitized (converted from analog to digital), encoded, and broadcasted.
The Bluetooth receiver inside the PA speaker receives the signal, and has to decode it, then transform it back to an analog signal so that the amplifier can use it.
All this process takes only a few milliseconds, but it creates a delay that’s long enough for you to hear it on the speakers. That’s where RF-based systems are much more efficient. They take the analog signal and transmit it immediately without digitizing or encoding it; hence there is no latency.
Final Thoughts
Any of the options explained in this post will help make powered pa speakers wireless. Having a wireless setup is very convenient for many reasons. I hope this post is helpful to you; thank you for reading my blog.